Glycolysis Can Best Be Described as
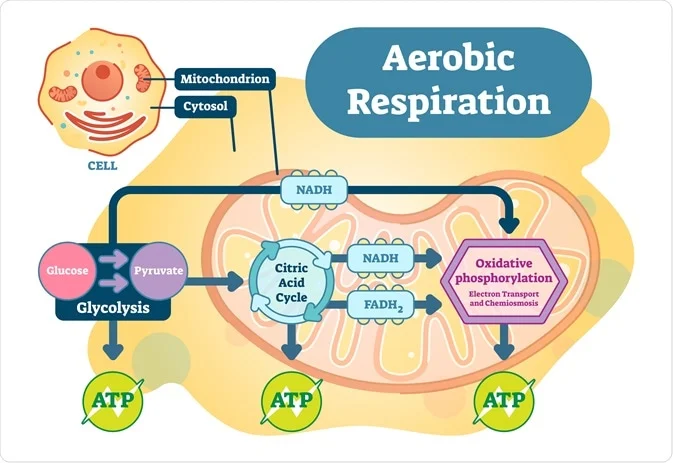
Some enzymatic steps are difficult to catalyze reversibly especially the ATP-driven. A conversion of glucose into carbon dioxide and water.
What Are Two Advantages Of Glycolysis Quora
Glycolysis is the process of breaking down glucose.

. Biology questions and answers. Before entering the Krebs cycle pyruvate is converted to. Skeletal muscles can survive because of anaerobic glycolysis.
Regulating these points in the pathway can prevent futile cycling. C conversion of pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide and water. Biochemical significance of Glycolysis.
Enter your email below and get the daily PCAT question sent straight to your inbox every morning. It is the only pathway that can act in an aerobic and anaerobic environment. Nearly all living organisms carry out glycolysis as part of their metabolism.
Glycolysis is best defined as a catabolic reaction based upon the ________. 1Cellular respiration can best be described as a using energy released from breaking high-energy covalent bonds in organic molecules to force ATP formation from ADP and phosphate. Which of the following statements about glycolysis is true.
DI Produces an ATP and an unphosphorylated fuel. Generally the bypass reactions are also irreversible. Cellular respiration can best be described as taking electrons from food and giving them to oxygen to make water and using the energy released to drive ATP formation.
Glycolysis yields two molecules of ATP free energy containing molecule two molecules of Pyruvic acid and two high energy electron carrying molecules of NADH. B taking electrons from food and giving them to phosphate to make ATP. Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism.
This metabolic phenotype is characterized by preferential dependence on glycolysis the process of conversion of glucose into pyruvate followed by lactate production for energy production in an oxygen-independent manner. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. B conversion of glucose into two molecules of pyruvic acid.
Altered energy metabolism is a biochemical fingerprint of cancer cells that represents one of the hallmarks of cancer. Nearly all living organisms carry out glycolysis as part of their metabolism. Glycolysis from Greek word glykys meaning sweet and lysis meaning dissolution or breakdown can be defined as the sequence of enzymatic reactions that in the cytosol also in the absence of oxygen leads to the conversion of one molecule of glucose a six carbon sugar to two molecules of pyruvate a three carbon compound with the concomitant.
Glycolysis is the first pathway used in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy. For each of the descriptive statements given here choose the best matching enzyme. Glycolysis is the only source of energy in erythrocytes.
It is a significant route for carbohydrate metabolism. It takes place in all the cells of the body. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm.
Aerobic and catabolic eAnaerobic and anabolic. It takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Catabolic and synthetic cGlycolytic and aerobic d.
Asked Aug 24 2019 in Anatomy Physiology by BioMan. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Question 16 1 pts Which of these terms best describes glycolysis and Krebs cycle.
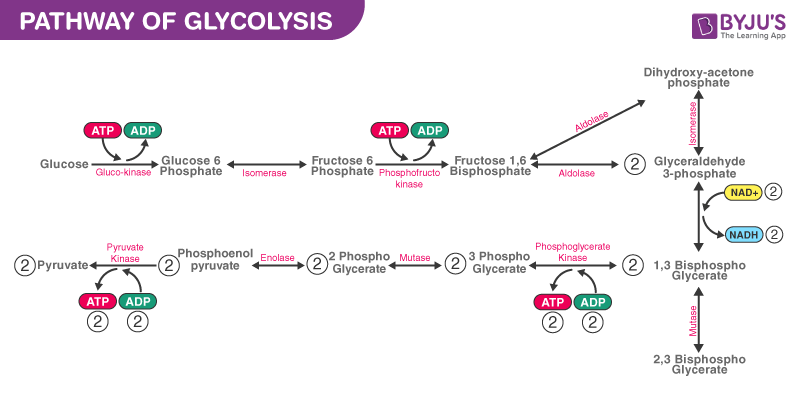
In glycolysis glucose a six carbon sugar is split into two molecules of a three-carbon sugar. C21C31 Glycolysis can best be described as which of the following kinds of pathways. Pellerin and Magistretti described this L-lactate production by astrocytes as aerobic glycolysis a term that thematically may be correct as lactate is produced despite the presence of oxygen but it is clearly confusing and misleading considering the fact that the L-lactate thus produced is concomitantly oxidized.
Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes. Anaerobic and catabolic b. Bypass the irreversible steps in glycolysis to progress through gluconeogenesis.
Why do irreversible steps exist in the first place. Get the daily question sent to your inbox. Glycolysis can take place with or without oxygen.
Glycolysis produces two molecules of pyruvate two molecules of ATP two molecules of NADH and two molecules of water. There are 10 enzymes involved in breaking down sugar. Note that the enzymes are abbreviated as we have abbreviated them in lecture.
The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate ATP and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NADH. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that. Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 into pyruvic acid CH 3 COCOOH.
D formation of sugar. Glycolysis is best defined as the breakdown of. Glycolysis is best defined as a catabolic reaction based upon the _____ asked Oct 16 2015 in Anatomy Physiology by Regiside A conversion of glucose into two molecules of pyruvic acid.
Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration during which glucose is modified to a 6-carbon sugar diphosphate and then split into two 3-carbon molecules. Glycolysis literally means Splitting Sugars. BYJUS Online learning Programs For K3 K10 K12 NEET.
The heart has been estimated to consume 20-30 times its own weight in ATP each day and mitochondria comprise about 30 of the volume of a cardiomyocyte. It was probably one of the earliest metabolic pathways to evolve since it is used by nearly all of the organisms on earth. Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism.
Endergonic reactions catabolic reactions oxidative phosphorylation reactions anabolic reactions Question 17 1 pts Which of these molecules can be described as the final or terminal electron acceptor. The process does not use oxygen and is therefore anaerobic. The enzymes of glycolysis can be described in many ways including by their substrates and products.
The same enzyme can be used multiple times. Glycolysis Glucose Catabolic Pathway. C taking electrons from food and giving them to oxygen to.
The process does not use oxygen and is therefore anaerobic processes that use oxygen are called aerobic.
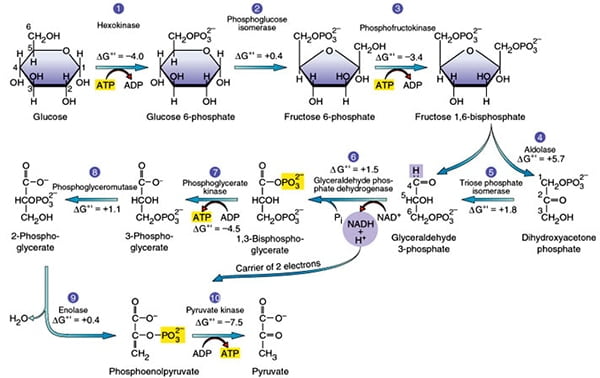
Glycolysis Explained In 10 Easy Steps With Diagrams
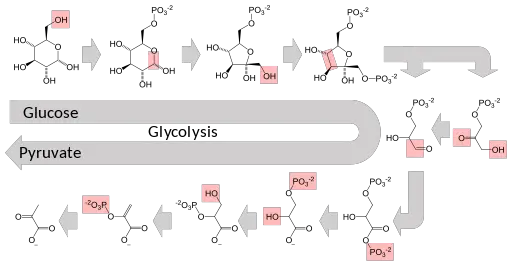
What Is Glycolysis Where Does It Take Place Pathway And Products
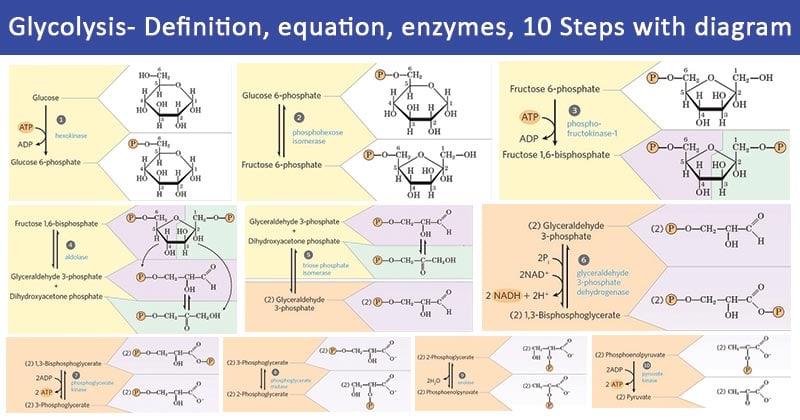
Glycolysis Definition Equation Enzymes 10 Steps Diagram

Cellular Respiration Definition Equation Cycle Process Reactants Products Britannica
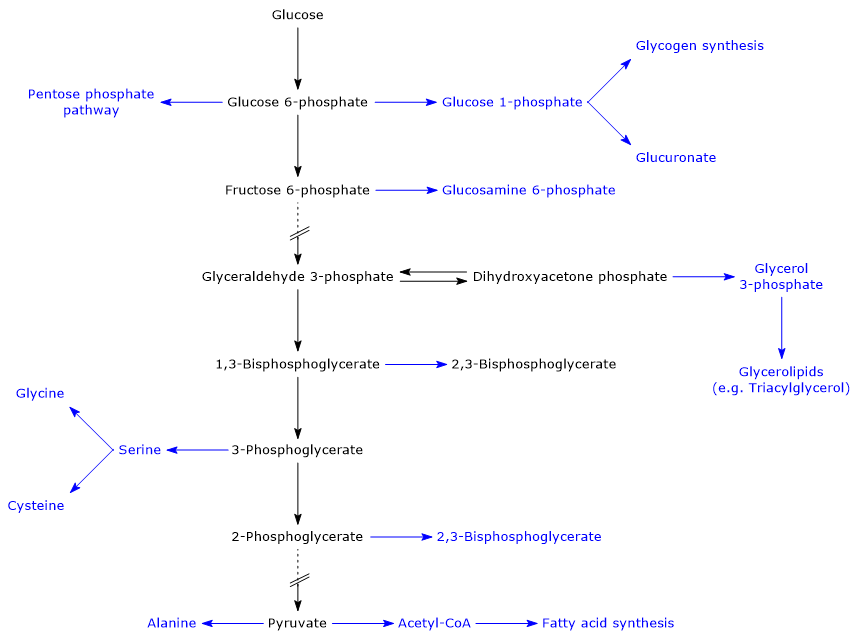
Glycolysis Steps Enzymes And Products Tuscany Diet
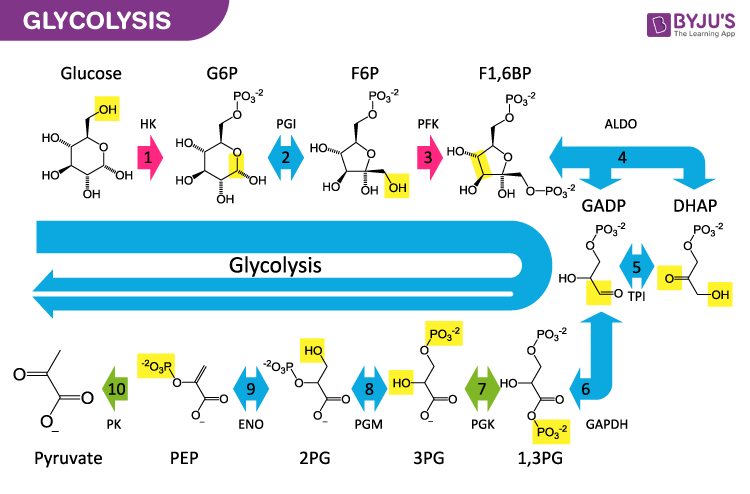
Glycolysis Definition And Glycolysis Pathway

An Overview Of Glycolysis By Which The Conversion Of Glucose To Download Scientific Diagram

Glycolysis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Glycolysis Introduction Pathway Diagram Summary Medical School Essentials Study Biology Medical School Studying
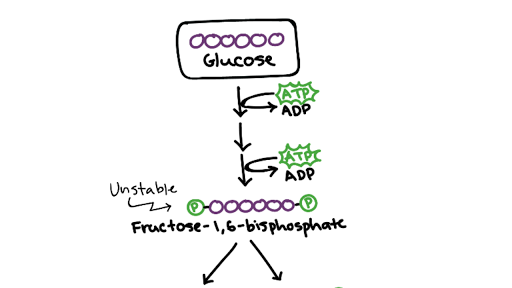
Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy
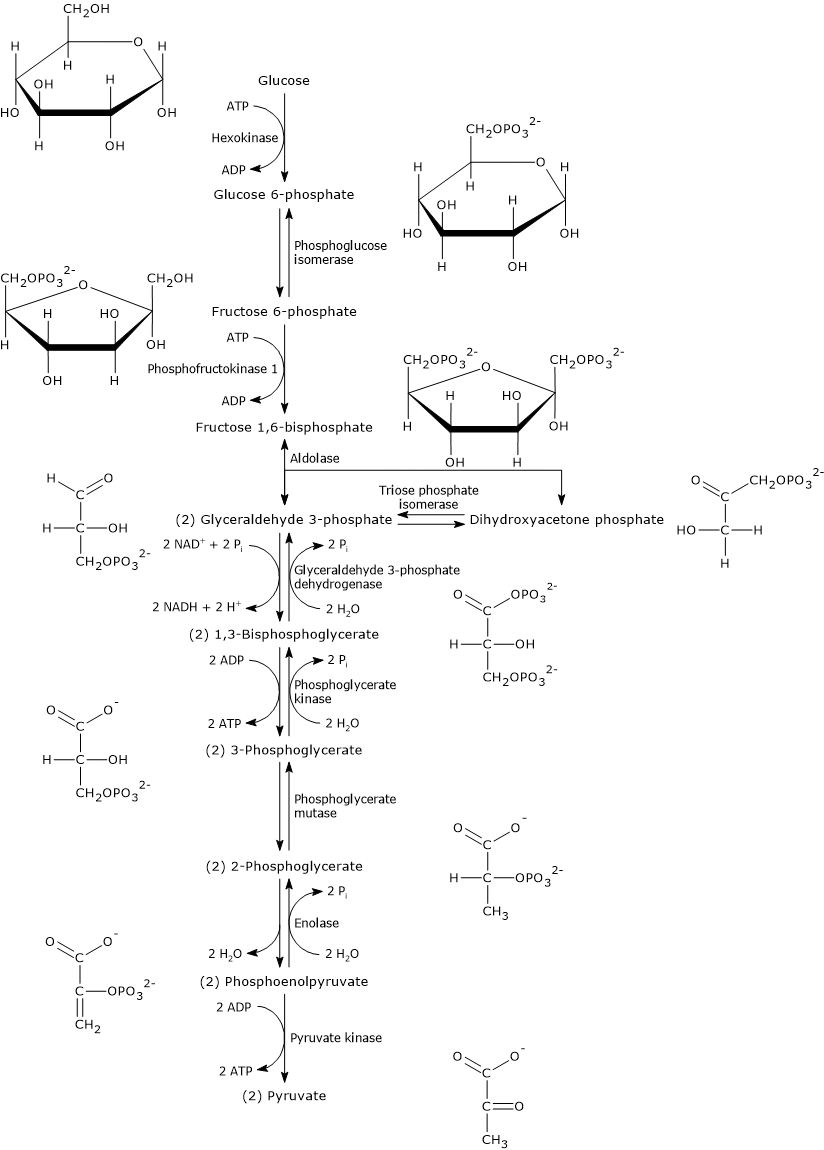
Glycolysis Steps Enzymes And Products Tuscany Diet

Lesson Explainer Glycolysis Nagwa
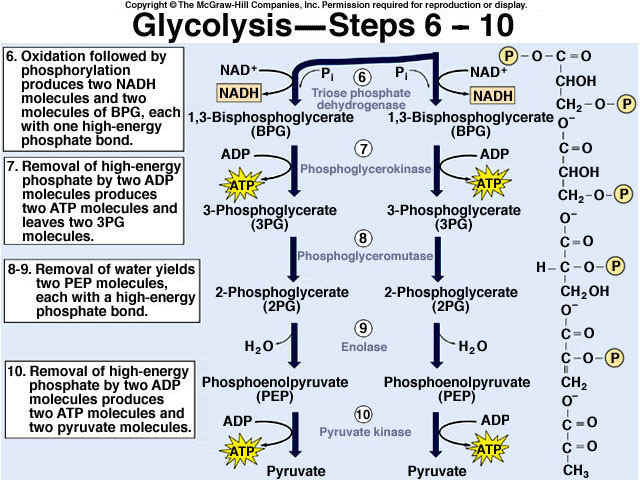
Topic 8 2 Cell Respiration Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green

Glycolysis Pathway Enzymes Regulation And Products Youtube

Topic 3 6 Cellular Respiration Biology Quiz Quizizz

Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy

Comments
Post a Comment